22 May An Introduction to Rafoxanide
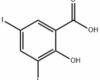
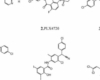
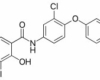
Rafoxanide is an antiparasitic active component used in veterinary medicine to treat cattle internal parasites (such as several roundworm species and liver flukes). It is not utilized to control agricultural or domestic pests. It belongs to the salicylanilide chemical class.
PERFORMANCE AGAINST PARASITES
Anthelmintic endoparasiticide is the mode of action.
The following veterinary parasites are primarily controlled: liver flukes and some gastrointestinal roundworms (e.g. Haemonchus, Bunostomum, Oesophagostomum, Chabertia)
The effectiveness against a certain parasite is determined on the delivery method and the dosage delivered.
SAFETY Oral LD50, acute*, rat: >2000 mg/kg Dermal LD50, acute*, rat: not detected
* These figures are for the active component. Toxicity must also be established for each formulation. Formulations are often far less hazardous than active components.
Withholding periods for meat, milk, eggs, and other products vary according on delivery type, dosage, and country regulations. In your country, check the product label.
Antiparasitic safety information:
- Antiparasitics are generally safe for domestic animals.
- Antiparasitics are generally safe for humans.
- Antiparasitics are generally safe for the environment.
FEATURES SPECIFIC
Rafoxanide is a long-established, broad-spectrum flukicide and nematicide. It is still used in cattle, primarily in ruminants, but it has been greatly outperformed by more effective chemicals. It is available as injectables and drenches, frequently in conjunction with a broad-spectrum nematicide (e.g. benzimidazoles, macrocyclic lactones, levamisole)
Rafoxanide's Efficacy
Rafoxanide is particularly effective against adult and immature (older than 6 weeks) liver flukes (Fasciola hepatica and Fasciola gigantica), a few gastrointestinal nematodes such as Haemonchus spp. and Bunostomum spp., and even against sheep bot fly-caused nasal myiases (Oestrus ovis).
Rafoxanide is ineffective against a variety of other gastrointestinal roundworms, lungworms (e.g., Dictyocaulus spp. ), eyeworms (e.g., Thelazia spp. ), and tapeworms.
Rafoxanide, unlike many other anthelmintics (e.g., imidazothiazoles, benzimidazoles, tetrahydropyrimidines), has a residual effect, which means it not only kills the parasites present in the host at the time of treatment, but also protects against re-infestation for a period of time (up to several weeks) depending on the dose and the specific parasite.
Rafoxanide pharmacokinetics
Rafoxanide is slowly absorbed into the circulation after oral intake. Maximum blood concentrations occur two to three days following therapy. Rafoxanide binds to more than 99 percent of plasma proteins. It is widely spread throughout the body, but it has a special affinity for the thyroid gland.
Excretion is rather sluggish, primarily via bile and feces, and mostly as the unmodified parent molecule. Urine contained less than 1% of the prescribed dosage. The half-life of excretion is approximately 10 days. Rafoxanide can be detected in the blood for up to 100 days following therapy.
Rafoxanide's mechanism of action
The molecular mechanism of action of salicylanilides, including rafoxanide, is not fully understood. They are all uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria of the cell, which disrupts the synthesis of ATP, the cellular “fuel.” This appears to be accomplished by inhibiting the activity of two enzymes involved in this process, succinate dehydrogenase and fumarate reductase. This reduces the parasite’s motility and, most likely, other processes.